|
General Settings and Handling of gvSIG |
|
 |
Settings |
| |
You can edit the general settings of gvSIG to your own needs, e.g. defining a standard projection (e.g. EPSG 4326 for WGS 84 geographical coordinates) ( Handbook Chapter 8, from page 572).
|
|
|
| |

|
Video: Changing Settings
Changing the settings of "Cartography", "Default Projection" and the "Selection Colour". |
|
|
 |
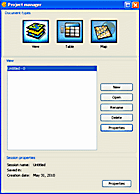
Project Manager
|
| |
After starting gvSIG, the Project Manager ( Handbook Chapter 2, from page 13) will be displayed. This is the main administration component in gvSIG. Here, new document types (View, Table, Map) can be generated or gvSIG project files (*.gvp) or templates (*.gvt) can be loaded or saved. It is also possible to edit the properties of the gvSIG project (name or projection type). |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Creating a new project
Starting a new project, adding data and saving the new project. |
|
| |
 |
Video: Load Project / Add Table
Loading a gvSIG-project file (*.gvp), adding data (*.csv) in table format. |
|
| |
 |
Video: New Layer / Map Export
Creating a new vector layer in *.shp format, defining polygons and editing colour settings as well as creating and exporting the map as *.pdf-file. |
|
|
 |
Selection Tools
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
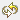 |
 |
| Information about feature |
Select by point |
Select by rectangle |
Select by polygon |
Clear selection |
Invert selection |
Show attributes of selected features |
One or several elements can be selected by graphical or alphanumerical requests. The default colour for selected data is yellow ( Handbook Chapter 4, from page 279). |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Selection Tools
Several ways of selecting features using different requests. |
|
|
 |
Zoom Functions
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Previous zoom |
Zoom in |
Zoom out |
Full extent |
Zoom in 1x |
Zoom out 1x |
Panning |
The gvSIG-Toolbar offers different zoom options to choose from (Handbook Chapter 4, Page 77). |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Zoom Functions
Demonstrating all main zoom functions. |
|
|
| |
| |
Processes |
|
 |
Transformation |
| |
Geo-data is often available in different projections. Before performing GIS-processes it is necessary to transform layers into the correct projection to ensure that all loaded layers overlap correctly. There are two ways of transforming: via "Geoprocess-Toolbox" or "on the fly" when adding a new layer. |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Transformation via Geoprocess Toolbox
Editing projection settings (current and target projection) and saving *.shp in the new projection. |
|
| |
 |
Video: Transformation "on the Fly"
Setting up a projection for the gvSIG-project, adding a layer referenced in a different projection, transforming it into the pre-set projection "on the fly" and saving the layer with its new projection as a new file. |
|
|
 |
Select and Export Vector-File from Layer
|
| |
It is possible to save selected features as a new *.shp-file which then can be loaded and edited separately. |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Select and Export Vector-File from Layer
Selecting a feature and exporting as a new *.shp-file. |
|
|
 |
Select by Location |
| |
|
 |
| Geoprocess Toolbox |
The "Geoprocess-Toolbox" offers a variety of processes for vector data such as merge, union, clip and many more. "Intersect" allows selecting features by their spatial location. The new layer will contain the features of the input cover that intersect with the clip cover ( Handbook Chapter 6, from page 417). |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Geoprocess Tools Intersect
Choosing the input, clip and output cover, generating and colouring the new *.shp-file. |
|
|
 |
Add Event Layer
|
| |
|
 |
| Add Event Layer |
Using the "Add Event Layer"-Tool allows loading an alphanumerical file (e.g. GPS-Coordinates saved as *.csv-file) with XY-Coordinates to a gvSIG-project. The data will be displayed as a point layer (Handbook Chapter 4, Page 127).
|
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Adding event layer
Loading a *.csv-file as a new table, using the "Add Event Layer"-Tool, defining "Latitude" and "Longitude" and saving as *.shp-point-file. |
|
|
 |
Editing
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Point |
Multipoint |
Line |
Arc |
Polyline |
Polygon |
Rectangle |
Circle |
Elipse |
To edit features, open the context-menu of a vector-layer by right-clicking on the layer-name in the "Table of Contents" and press "Start Editing". The editable layer will be marked red and new icons will be added to the toolbar offering different editing options.
New features can be added to the activated layer or existing features can be rearranged or deleted. The editing process will be completed and changings saved when clicking the "Finish Editing"-Button in the context menu of the activated layer (Handbook Chapter 5, Page 315). |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Point Type
Start editing, deleting point features, defining new point features, calculating XY-Coordinates, finish editing. |
|
| |
 |
Video: Line Type
Start editing line type feature, defining new line, deleting feature, rearranging vertex, finish editing. |
|
| |
 |
Video: Polygon Type
Start editing polyline type feature, defining new polyline, splitting feature, calculating area, finish editing. |
|
|
 |
Calculate Expression
|
| |
|
 |
| Calculate Expression |
For each vector layer an attribute table stores alphanumerical information about all features (point, line, polygon) of the layer. Each vector feature is referred to a line in the attribute table which can be edited and values calculated using the algorithms available through the field calculator ("Expression").
The function "Manage Fields" ("Table" -> "Manage Fields") allows adding, removing and renaming fields of the attribute table (chapter 5, from page 382). |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Point Type
Opening the table of a point type shapefile, managing the attribute table, adding fields to the table, calculating XY-Coordinates, finish editing. |
|
| |
 |
Video: Line Type
Editing the attribute table of a line type shapefile, calculating perimeter, finish editing. |
|
| |
 |
Video: Polygon Type
Managing the attribute table of a polygon type shapefile, adding a field to the table, calculating the area of polygons, finish editing. |
|
|
| |
| |
Publish |
|
 |
Layer Properties: Symbols |
| |
The "Symbol Selector" allows visualising relations and meanings of displayed features ( chapter 4, from page 213). |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Point Type
Changing the symbol colour, size and shape-style of point type features as well as using a picture symbol and symbols by classification. |
|
| |
 |
Video: Line Type
Changing colour and width of pre-set styles as well as generating a new line-style. |
|
| |
 |
Video: Polygon Type
Changing colour and style using pre-set brushes as well as generating own brushes and symbols by classification. |
|
|
 |
Layer Properties: Labelling
|
| |
To label vector features in the "View" or the "Map" use the "Labelling"-Function of the "Layer Properties" and choose one of two types of labelling:
- Static labelling (Using attributes from the layer's attribute table)
- Advanced labelling (User defined)
To activate labelling, tick the "Enable Labelling" checkbox (chapter 4, from page 263). |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Point Type
Labelling with "User defined labels", defining the font, text size, expression and placement properties. |
|
| |
 |
Video: Line Type
Labelling with "User defined labels", defining the font and expression and setting up placement properties (Orientation, Position). |
|
| |
 |
Video: Polygon Type
Labelling with "User defined labels", defining the font, expression and placement properties. |
|
|
 |
Locator Map
|
| |
The "Locator Map" is an overview map below the "Table of Contents" in the "View"-Window and indicates the working area (main window zoom).
Click on “View” in the menu bar and select “Configure locator map” to add a map (e.g. world map) (chapter 4, from page 80). |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Locator Map
Adding a shapefile as a layer to show up in the "Locator Map". Creating a map, inserting the main frame and the locator frame. |
|
|
 |
Map Preperation
|
| |
As gvSIG-document types are connected with each other, data can be prepared in the "View" and transferred to and arranged in the "Map" to generate a layout for printing. |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Map Preparation
Renaming layers to be displayed in the map (names of layers will be displayed as legend elements of the map), starting a new "Map", setting up "Map Properties" (chapter 7, from page 550). |
|
|
 |
Map Creation
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Insert View |
Insert Locator |
Insert Legend |
Insert Scale |
Insert North |
Insert Grid |
A map is a visual representation of an area highlighting relationships between places (areas, regions...) and objects (buildings, streets, wells...).
A map should at least consist of "Map Title", "Map Legend", "Scale Information" and "Northing" (chapter 7, from page 550). |
|
|
| |
 |
Video: Map Creation
Adding a headline with the "Welthungerhilfe-Logo", title and background colour, adding the main view, map legend, northing and scale bar. Using the "size/position" dialogue to get an accurate map layout.
Exporting the map as *.pdf. |
| |
|
|
|
|